| Citation: | Feng Jiang, Tao Feng, Yongbin Zhu, Chengliang Xia, Chengyan Liu, et al. Structure, Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of High Entropy Selenides Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3. Materials Lab 2022, 1, 220045. doi: 10.54227/mlab.20220045 |
Structure, Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of High Entropy Selenides Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3
-
Abstract
Introducing magnetic elements or nanoparticles into the thermoelectric matrix is of great importance to regulate the thermoelectric performance and evaluate the magnetic-thermoelectric effect. While, the limitation of solid solution ability of magnetic elements in thermoelectric materials impedes the development of magnetic thermoelectric matrix. Herein, we have applied high entropy strategy to alloy a large amount of Cr elements into the Bi2Se3 sub-lattice, and successfully obtained a single-phase magnetic thermoelectric material in the nominal composition of Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3. The Magnetization loop curves of Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 sample shows obvious ferromagnetic behavior with a coercivity of 2000 Oe and residual magnetization of 0.22 emu g−1 at 2 K. The temperature dependence of zero-field-cooled magnetic susceptibility and field-cooled magnetic susceptibility reveals a transition from ferromagnetism to paramagnetism at 61 K. These findings indicate that a magnetic Bi2Se3 based thermoelectric material is successfully obtained. The corresponding structure, magnetic and thermoelectric properties are also carefully discussed. This work offers a new avenue to achieve a magnetic thermoelectric material through high entropy strategy.
-
Keywords:
- Selenides /
- Magnetic /
- High-entropy /
- Thermoelectric
-
-
References
1. R. P. Chasmar and R. Stratton, J. Electro. Control, 1959, 7, 52 2. J. He and T. M. Tritt, Science, 2017, 357, eaak9997 3. W. S. Liu, X. Qian, C.-G. Han, Q. K. Li and G. Chen, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 118, 020501 4. Y. Z. Pei, X. Y. Shi, A. LaLonde, H. Wang, L. D. Chen and G. J. Snyder, Nature, 2011, 473, 66 5. H. L. Yu, A. R. Shaikh, F. Xiong and Y. Chen, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 9889 6. H. Usui and K. Kuroki, J. Appl. Phys., 2017, 121, 165101 7. B. Poudel, Q. Hao, Y. Ma, Y. C. Lan, A. Minnich, B. Yu, X. Yan, D. Z. Wang, A. Muto, D. Vashaee, X. Y. Chen, J. M. Liu, M. S. Dressel, G. Chen and Z. F. Ren, Science, 2008, 320, 634 8. W. S. Liu, X. Yan, G. Chen and Z. F Ren, Nano Energy, 2012, 1, 42 9. T. J. Zhu, L. P. Hu, X. B. Zhao and J. He, Adv. Sci., 2016, 3, 1600004 10. J. Li, S. Zhang, F. Jia, S. Q. Zheng, X. L. Shi, D. Q. Jiang, S. Y. Wang, G. W. Lu, L. M. Wu and Z.-G. Chen, Mater. Today Phys., 2020, 15, 100269 11. T. Zhao, K. Zhao, Q. Y. Liu, X. S. Yang and Y. Zhao, J. Appl. Phys., 2020, 127, 155101 12. P. J. Sun, K. R. Kumar, M. Lyu, Z. Wang, J. S Xiang and W. Q. Zhang, The Innovation, 2021, 2, 100101 13. S. Hébert, R. Daou, A. Maignan, S. Das, A. Banerjee, Y. Klein, C. Bourges, N. Tsujii and T. Mori, Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater., 2021, 22, 583 14. J. K. Furdyna, J. Appl. Phys., 1988, 64, R29 15. T. Feng, P. S. Wang, Z. J. Han, L. Zhou, W. Q. Zhang, Q. H. Liu and W. S. Liu, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, 2200931 16. A. Bentien, S. Johnsen, G. K. H. Madsen, B. B. Iversen and F. Steglich, EPL, 2007, 80, 17008 17. Y. Zheng, T. Lu, M. M. H. Polash, M. Rasoulianboroujeni, N. Liu, M. E. Manley, Y. Deng, P. J. Sun, X. L. Chen, R. P. Hermann, D. Vashaee, J. P. Heremans and H. Zhao, Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, 9461 18. J. Z. Wu, F. C. Liu, C. Liu, Y. Wang, C. C. Li, Y. F. Lu, S. Matsuishi and H. Hosono, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2001815 19. T. Okuda, N. Jufuku, S. Hidaka and N. Terada, Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 72, 144403 20. Z. C. Wei, C. Y. Wang, J. Y. Zhang, J. Yang, Z. L. Li, Q. D. Zhang, P. F. Luo, W. Q. Zhang, E. K. Liu and J. Luo, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 20653 21. F. Ahmed, N. Tsujii and T. Mori, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 7545 22. W. Y. Zhao, Z. Y. Liu, P. Wei, Q. J. Zhang, W. T. Zhu, X. L. Su, X. F. Tang, J. H. Yang, Y. Liu, J. Shi, Y. M. Chao, S. Q. Lin and Y. Z. Pei, Nat. Nanotechnology, 2017, 12, 55 23. W. Y. Zhao, Z. Y. Liu, Z. G. Sun, Q. J. Zhang, P. Wei, X. Mu, H. Y. Zhou, C. C. Li, S. F. Ma, D. Q. He, P. X. Ji, W. T. Zhu, X. L. Nie, X. L. Su, X. F. Tang, B. G. Shen, X. L. Dong, J. H. Yang, Y. Liu and J. Shi, Nature, 2017, 549, 247 24. N. Jia, J. Cao, X. Y. Tan, J. F. Dong, H. F. Liu, C. K. I. Tan, J. W. Xu, Q. Y. Yan, X. J. Loh and A. Suwardi, Mater. Today Phys., 2021, 21, 100519 25. H. Takaki, K. Kobayashi, M. Shimono, N. Kobayashi, K. Hirose, N. Tsujii and T. Mori, Mater. Today Phys., 2017, 3, 85 26. D. Chen, F. Jiang, L. Fang, Y.-B. Zhu, C.-C. Ye and W.-S. Liu, Rare Met., 2022, 41, 1543 27. F. Jiang, C. L. Xia, Y. B. Zhu, Z. J. Han, C. Y. Liu, J. T. Xia, Y. Chen and W. S. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 118, 193903 28. T. P. Bailer, R. Lu, P. F. P. Poudeu and C. Uher, Mater. Today Phys., 2019, 11, 100155 29. F.-H. Sun, S. F. Ma, W. Y. Zhao, C. C. Li, X. H. Sang, P. Wei and Q. J. Zhang, Rep. Prog. Phys, 2021, 84, 096501 30. T. Feng, L. Q. Li, Q. Shi, Y. L. Zhang and G. S. Li, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2020, 145, 106040 31. T. Feng, L. Q. Li, Q. Shi, X. L. Che, X. L. Xu and G. S. Li, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2018, 119, 127 32. D. A. McQuarrie, Statistical Mechanics, University Science Books, USA, 2000. 33. Y. Tokura, Y. Taguchi, Y. Okada, Y. Fujishima, T. Arima, K. Kumagai and Y. Iye, Phys, Rev. Lett., 1993, 70, 2126 34. D. Pines and P. Nozieres, The Theory of Quantum Liquids, W. A. Benjamin, USA, 1966. 35. R. Fortulan, S. A. Yamini, C. Nwanebu, S. W. Li, T. Baba, M. J. Reece and T. Mori, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2022, 5, 3845 36. T. Teramoto, T. Komine, M. Kuraishi and R. Sugita, J. Appl. Phys, 2008, 103, 043717 37. M. S. Akhanda, S. E. Rezaei, K. Esfarjani S. Krylyuk, A. V. Davydov, and M. Zebarjadi, Phys. Rev. Mater., 2021, 5, 015403 -
Rights and permissions
This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Information
Article Metrics
-
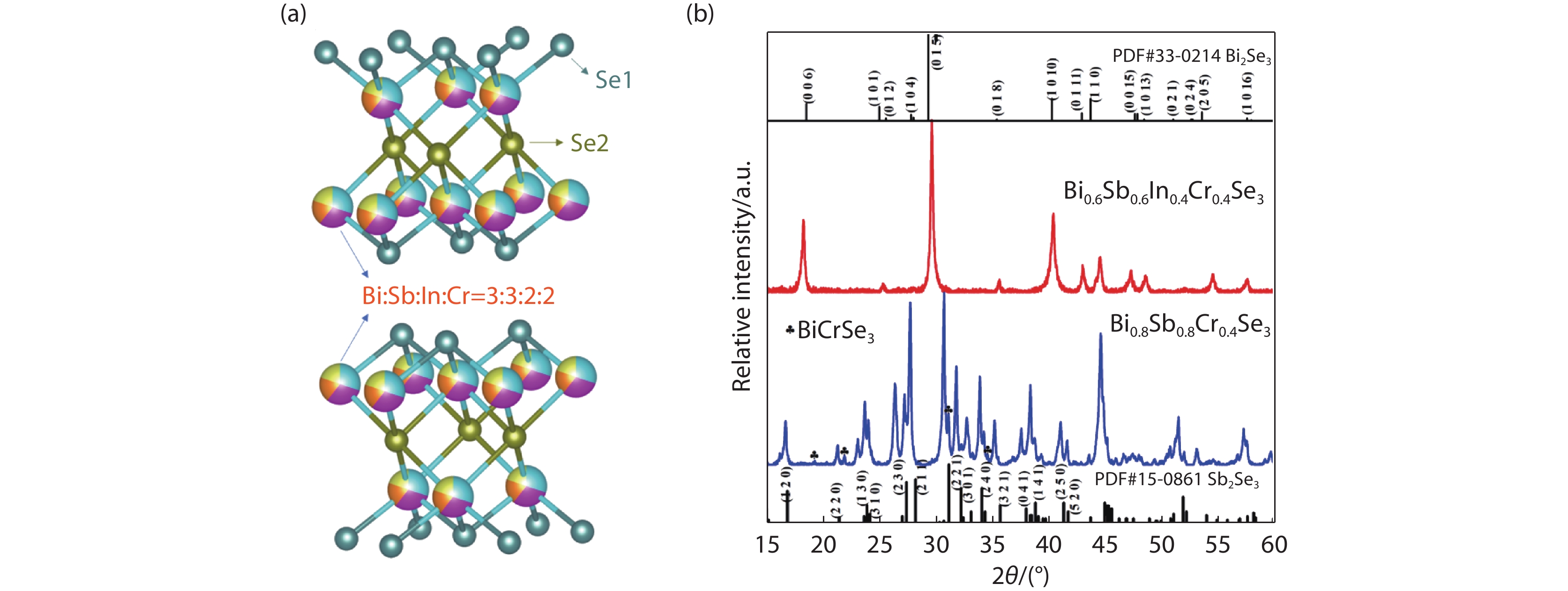
Figure 1.
(a) Crystal structure of the as-fabricated Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 high entropy selenides. Cyan for Se1, Brown for Se2, Mixed color for randomly distributed Bi, Sb, In, and Cr. (b) XRD patterns of pristine Bi0.8Sb0.8Cr0.4Se3 and Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3. The insert symbol represented the secondary phase BiCrSe3 (PDF#51-0750) in Bi0.8Sb0.8Cr0.4Se3 material.
-
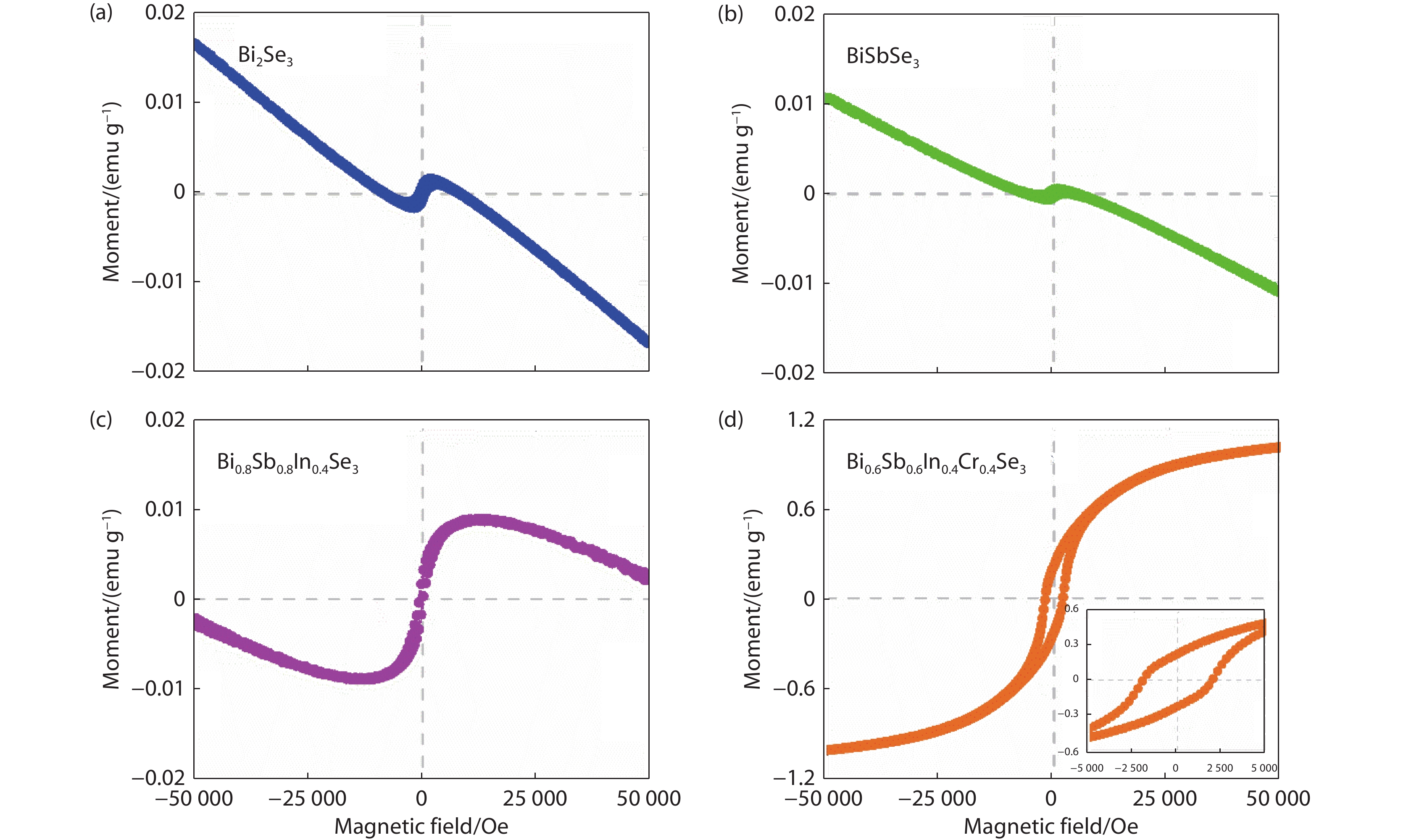
Figure 2.
M-H curves of (a) Bi2Se3, (b) BiSbSe3, (c) Bi0.8Sb0.8In0.4Se3, and (d) Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 at 2 K.
-
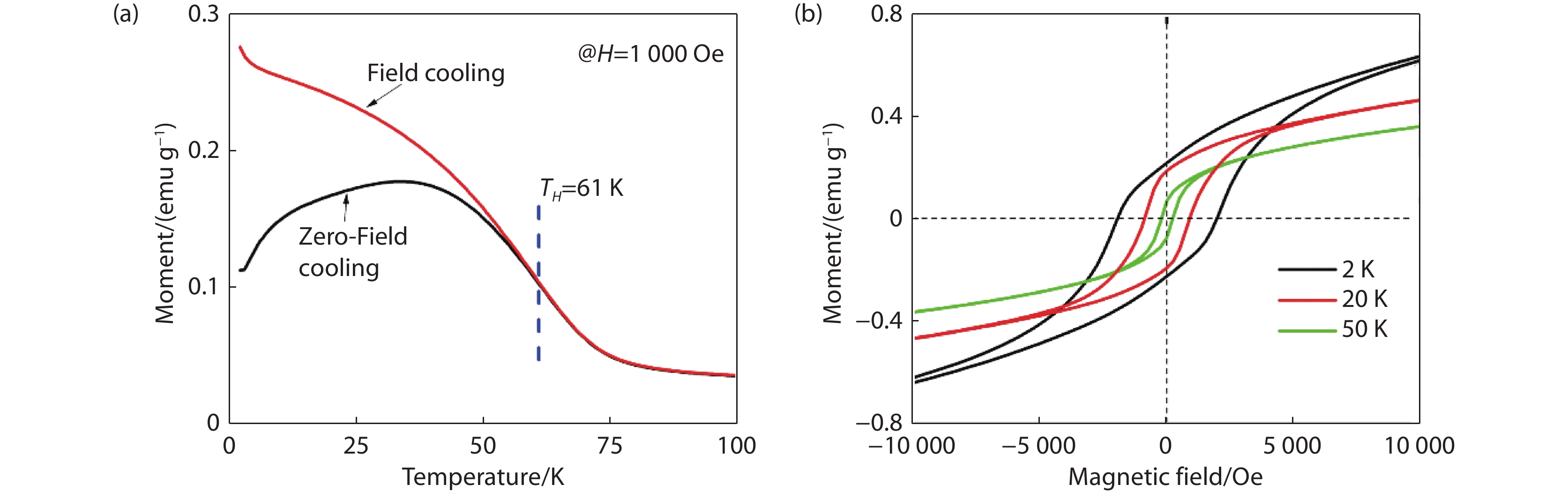
Figure 3.
(a) Zero-Field cooling and Field cooling curves of pristine Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 with a magnetization of
1000 Oe. (b) M-H curves of pristine Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 at different temperatures (2 K, 20 K and 50 K). -
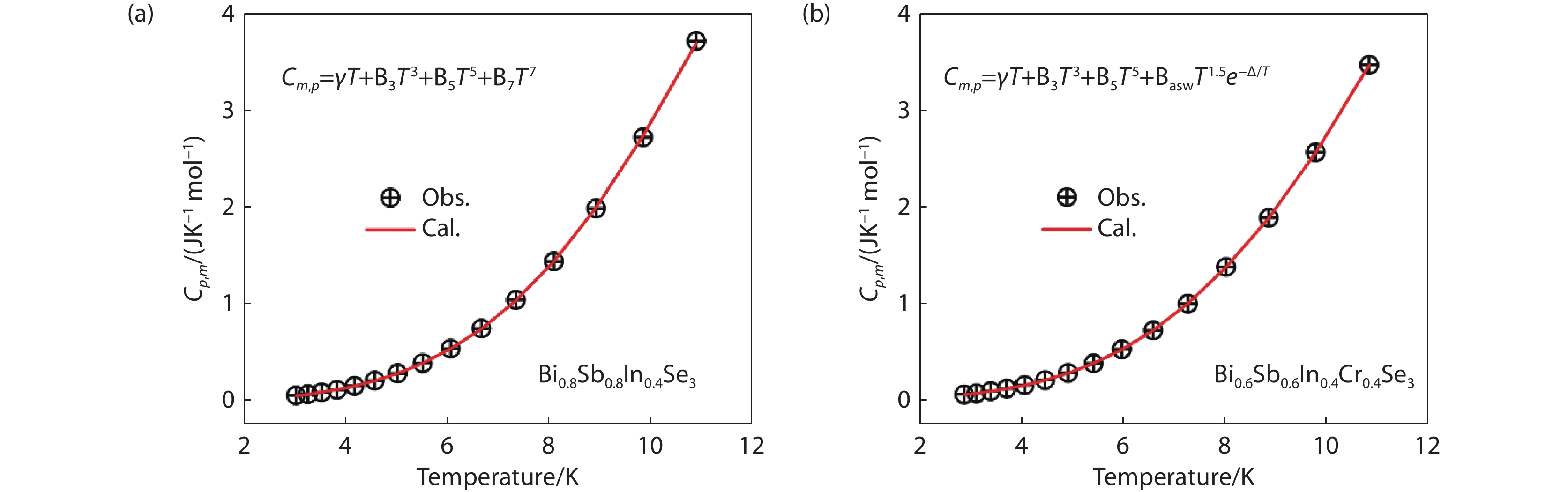
Figure 4.
Heat capacity of (a) Bi0.8Sb0.8In0.4Se3 and (b) Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 as a function of temperature over the range of 3 to 11 K. The dots stand for the experimental data, and the red line represents the fitted result.
-
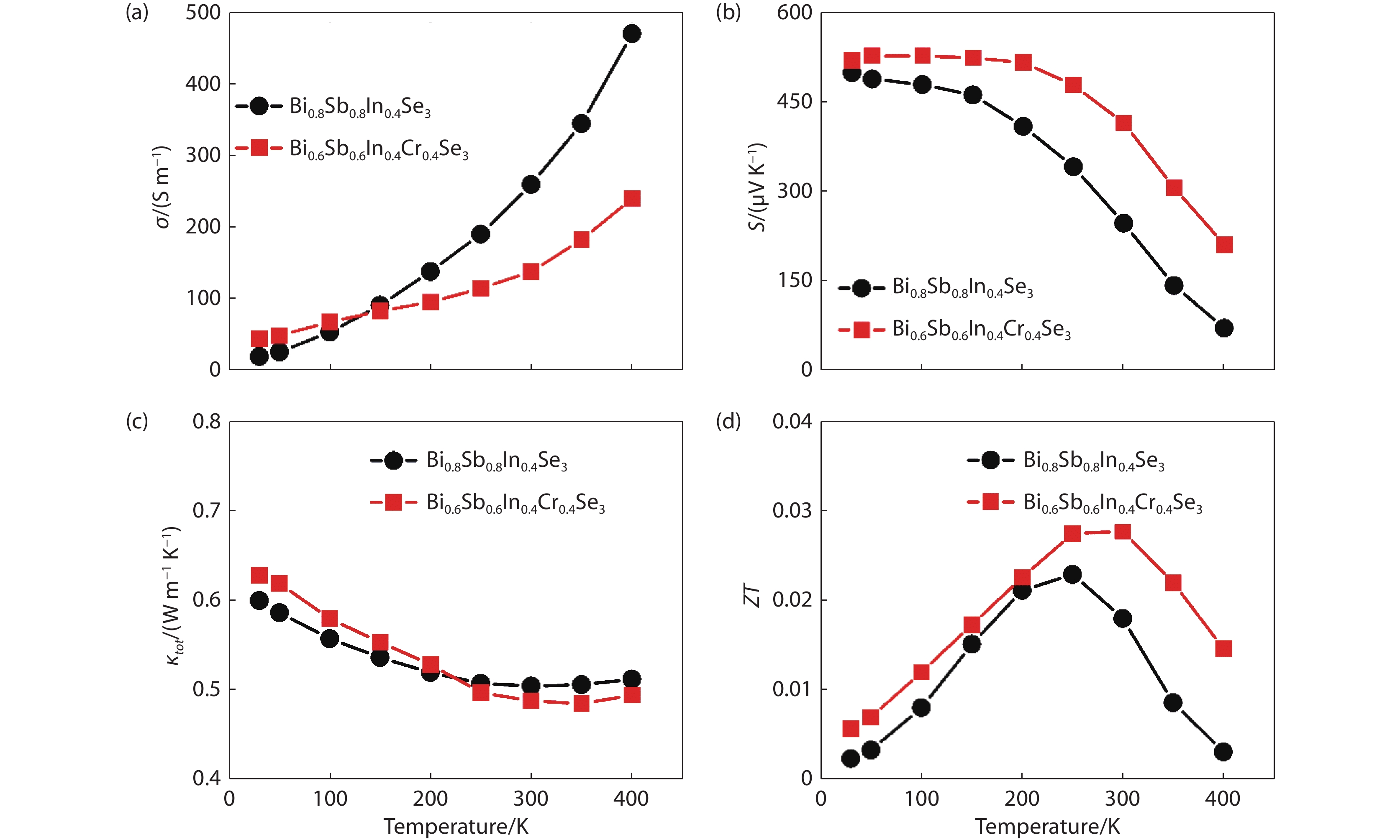
Figure 5.
Temperature dependent thermoelectric properties of Bi0.8Sb0.8In0.4Se3 and Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 samples: (a) electrical conductivity, (b) Seebeck coefficient, (c) thermal conductivity, and (d) ZT.
-
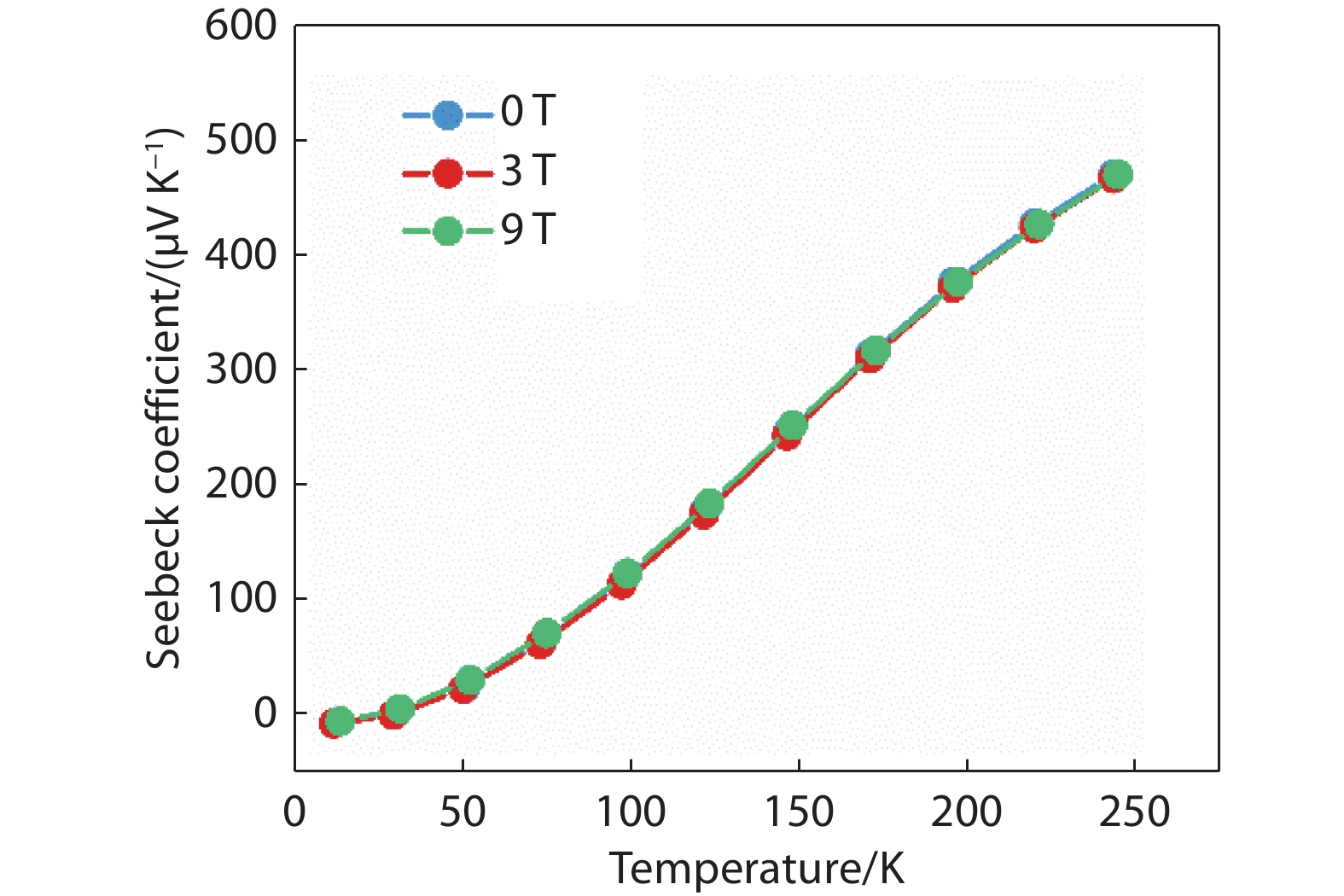
Figure 6.
The Magneto-Seebeck coefficient of Bi0.6Sb0.6In0.4Cr0.4Se3 at 0, 3, and 9 Tesla in a temperature range of 2 K - 250 K.


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: