| Citation: | Wang-Qi Bao, Xing Yang, Tian-En Shi, Ze Li, Yi-Xin Zhang, Jing Feng, Zhen-Hua Ge. The role of Ag8GeS6 addition in p-type SnSe with enhanced thermoelectric properties[J]. Materials Lab, 2024, 3(3): 240011. doi: 10.54227/mlab.20240011 |
The role of Ag8GeS6 addition in p-type SnSe with enhanced thermoelectric properties
-
Abstract
Polycrystalline SnSe is anticipated to perform in thermoelectric applications within the intermediate temperature range due to its superior machinability and more accessible synthesis conditions relative to single-crystal SnSe. Nonetheless, the subpar electrical properties of SnSe present a significant challenge in strengthening its electrical transport performance while preserving its intrinsic low heat conductivity, hence impeding the advancement of polycrystalline SnSe performance. This work examined the alterations in thermoelectric characteristics following the introduction of Ag8GeS6 compound into SnSe. When the Ag8GeS6 enters the SnSe matrix, the carrier concentration increases due to the Ag+ substitution, and the n-type second phase Ag2Se in the SnSe matrix acts as an electron attraction center also play an important role. Therefore, the electrical transport property increases from 306 μW m−1 K−2 of the pristine sample to 617 μW m−1 K−2 of the SnSe doped with 0.25 weight percent Ag8GeS6 sample at 873 K. Besides, the thermal conductivity is kept by the point defects, second phase, and dislocations, which can enhance the phonon scattering, and a low lattice thermal conductivity of 0.3 W m−1 K−1 for the SnSe doped with 0.125 weight percent Ag8GeS6 sample is obtained at 873 K. Consequently, a peak ZT value of 1.3 at 873 K and a high average ZT value of 0.57 from 323-873 K were achieved for SnSe doped with 0.25 weight percent Ag8GeS6. This demonstrates the potential in the field of power generation.
-
-
References
1. L.-D. Zhao, M. G. Kanatzidis, J. Materiomics, 2016, 2, 101 2. Y. Xiao, L.-D. Zhao, Science, 2020, 367, 1196 3. B. Qin, M. G. Kanatzidis, L-D. Zhao, Science, 2024, 386, 285 4. B. Qin, L.-D. Zhao, Science, 2022, 378, 832 5. Z.-G. Chen, W.-D. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 121, 256 6. J. Peng, F. Ge, W. Han, T. Wu, J. Tang, Y. Li, C. Wang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2025, 212, 272 7. Z.-G. Chen, X. Shi, L.-D. Zhao, J. Zou, Prog. Mater Sci., 2018, 97, 283 8. J. He, T. M. Tritt, Science, 2017, 357, 1369 9. B. Jiang, W. Wang, S. Liu, Y. Wang, C. Wang, Y. Chen, L. Xie, M. Huang, J. He, Science, 2022, 377, 208 10. F. Z. Zhang, D. Wu, J. He, Mat. Lab, 2022, 1, 220012 11. Y.-P. Wang, B.-C. Qin, D.-Y. Wang, T. Hong, X. Gao, L.-D. Zhao, Rare Met., 2021, 40, 2819 12. N. Xin, Y. Li, H. Shen, L. Shen, G. Tang, J. Materiomics, 2022, 8, 475 13. Y. Qin, T. Xiong, J.-F. Zhu, Y.-L. Yang, H.-R. Ren, H.-L. He, C.-P. Niu, X.-H. Li, M.-Q. Xie, T. Zhao, J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11, 1671 14. Y. Wu, X. Zhang, B. Wang, J. Liang, Z. Zhang, J. Yang, X. Dong, S. Zheng, H.-Z. Zhao, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 101, 71 15. Y.-X. Zhang, Q. Lou, Z.-H. Ge, S.-W. Gu, J.-X. Yang, J. Guo, Y.-K. Zhu, Y. Zhou, X.-H. Yu, J. Feng, J. He, Acta Mater., 2022, 233, 117972 16. H. Hu, Y. Ju, J. Yu, Z. Wang, J. Pei, H.-C. Thong, J.-W. Li, B. Cai, F. Liu, Z. Han, B. Su, H.-L. Zhuang, Y. Jiang, H. Li, Q. Li, H. Zhao, B.-P. Zhang, J. Zhu, J.-F. Li, Nat. Mater., 2024, 23, 527 17. C. Li, L. Wu, Y.-X. Zhang, J. Guo, J. Feng, Z.-H. Ge, Mat. Lab, 2022, 1, 220014 18. C. Tang, D. Liang, H. Li, K. Luo, B. Zhang, J. Adv. Ceram., 2019, 8, 209 19. Y.-X. Zhang, Q.-Y. Huang, X. Yan, C.-Y. Wang, T.-Y. Yang, Z.-Y. Wang, Y.-C. Shi, Q. Shan, J. Feng, Z.-H. Ge, Nat. Commun., 2024, 15, 2736 20. C. Chang, M. Wu, D. He, Y. Pei, C.-F. Wu, X. Wu, H. Yu, F. Zhu, K. Wang, Y. Chen, L. Huang, J.-F. Li, J. He, L.-D. Zhao, Science, 2018, 360, 778 21. L.-D. Zhao, C. Chang, G. Tan, M. G. Kanatzidis, Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9, 3044 22. L. Zhang, J. Wang, Q. Sun, P. Qin, Z. Cheng, Z. Ge, Z. Li, S. Dou, Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7, 1700573 23. H. Zhang, X. Liu, J. Wang, B. Zhang, J. Chen, L. Yang, G. Wang, M. Li, Y. Zheng, X. Zhou, G. Han, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 37201 24. Y. Gong, P. Ying, Q. Zhang, Y. Liu, X. Huang, W. Dou, Y. Zhang, D. Li, D. Zhang, T. Feng, M. Wang, G. Chen, G. Tang, Energy Environ. Sci., 2024, 17, 1612 25. B. Qin, Y. Zhang, D. Wang, Q. Zhao, B. Gu, H. Wu, H. Zhang, B. Ye, S. J. Pennycook, L.-D. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 5901 26. A. I. Pogodin, M. J. Filep, V. Y. Izai, O. P. Kokhan, P. Kúš, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2022, 168, 110828 27. H. Liang, Q. Lou, Y.-K. Zhu, J. Guo, Z.-Y. Wang, S.-W. Gu, W. Yu, J. Feng, J. He, Z.-H. Ge, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 45589 28. Y. Yu, D.-S. He, S. Zhang, O. Cojocaru-Mirédin, T. Schwarz, A. Stoffers, X.-Y. Wang, S. Zheng, B. Zhu, C. Scheu, D. Wu, J.-Q. He, M. Wuttig, Z.-Y. Huang, F.-Q. Zu, Nano Energy, 2017, 37, 203 29. P. Carruthers, Phys. Rev., 1959, 114, 995 30. S. I. Kim, K. H. Lee, H. A. Mun, H. S. Kim, S. W. Hwang, J. W. Roh, D. J. Yang, W. H. Shin, X. S. Li, Y. H. Lee, G. J. Snyder, S. W. Kim, Science, 2015, 348, 109 31. H. Leng, M. Zhou, J. Zhao, Y. Han, L. Li, J. Electron. Mater., 2016, 45, 527 32. C.-L. Chen, H. Wang, Y.-Y. Chen, T. Day, G. J. Snyder, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 11171 33. M. Cutler, N. F. Mott, Phys. Rev., 1969, 181, 1336 34. J. Zhu, X. Zhang, M. Guo, J. Li, J. Hu, S. Cai, W. Cai, Y. Zhang, J. Sui, npj Comput. Mater., 2021, 7, 116 35. T. A. Wubieneh, C.-L. Chen, P. C. Wei, S.-Y. Chen, Y.-Y. Chen, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 114825 36. T.-R. Wei, C.-F. Wu, X. Zhang, Q. Tan, L. Sun, Y. Pan, J.-F. Li, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 30102 37. E. K. Chere, Q. Zhang, K. Dahal, F. Cao, J. Mao, Z. Ren, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 1848 38. H. Wang, H. Hu, N. Man, C. Xiong, Y. Xiao, X. Tan, G. Liu, J. Jiang, Mater. Today Phys., 2021, 16, 100298 39. C. Li, H. Wu, B. Zhang, H. Zhu, Y. Fan, X. Lu, X. Sun, X. Zhang, G. Wang, X. Zhou, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 8446 40. H. Guo, H. Xin, X. Qin, J. Zhang, D. Li, Y. Li, C. Song, C. Li, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 689, 87 41. C.-H. Chien, C.-C. Chang, C.-L. Chen, C.-M. Tseng, Y.-R. Wu, M.-K. Wu, C.-H. Lee, Y.-Y. Chen, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 34300 -
Rights and permissions
This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Information
Article Metrics
-
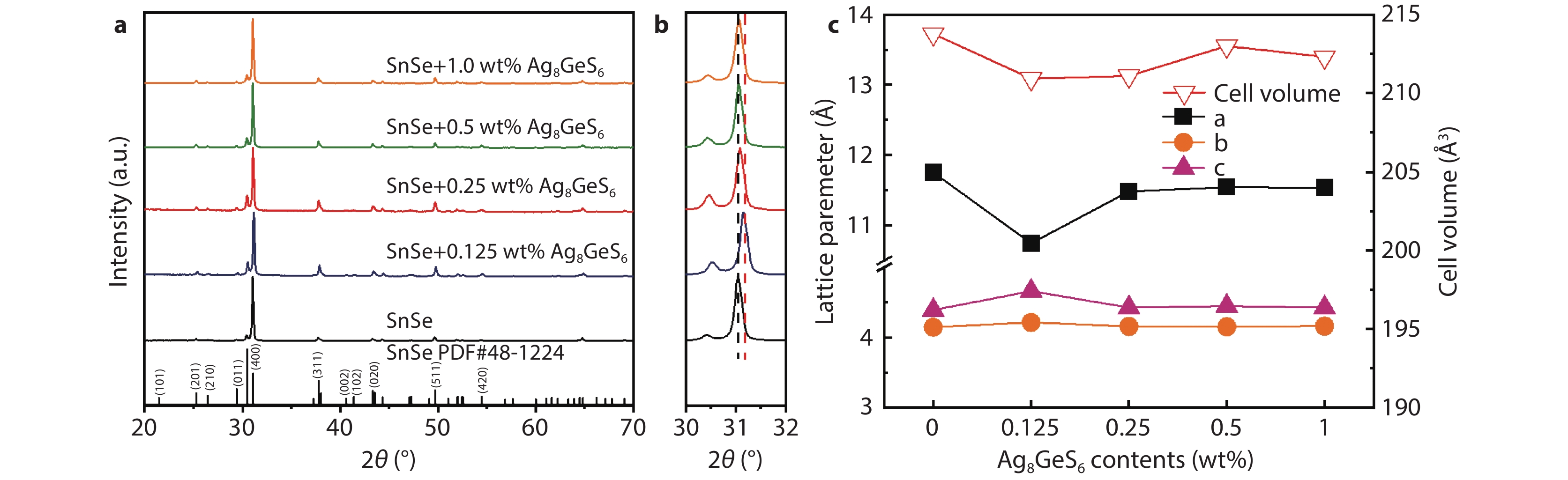
Figure 1.
a XRD patterns of the SnSe + x wt% Ag8GeS6 (x = 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0) samples; b enlarged XRD patterns in a 2-Theta range of 30°–32°; c the lattice parameters of the SnSe + x wt% Ag8GeS6 (x = 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0) samples.
-
Figure 2.
FESEM images of the fractured surfaces a x = 0, b x = 0.125, c x = 0.25, d x = 0.5, e x = 1.0, and f the experimental density and relative density for the pristine SnSe +x wt% Ag8GeSe6 (x = 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0) bulk samples.
-
Figure 3.
EMPA-mapping information for the SnSe + 0.25 wt% Ag8GeS6 sample a BSE image and b–f the elements of Sn, Se, Ag, Ge and S, respectively.
-
Figure 4.
TEM information for the SnSe + 0.25 wt% Ag8GeS6 sample: a Low-resolution image, b1, b3 high-resolution image, b2 FFT image of b1, c1 high-resolution image, c2 IFFT image of c1, c3 GPA analysis of c1, the EDS-mapping of d Sn, e Se, f Ag, g Ge and h S, respectively.
-
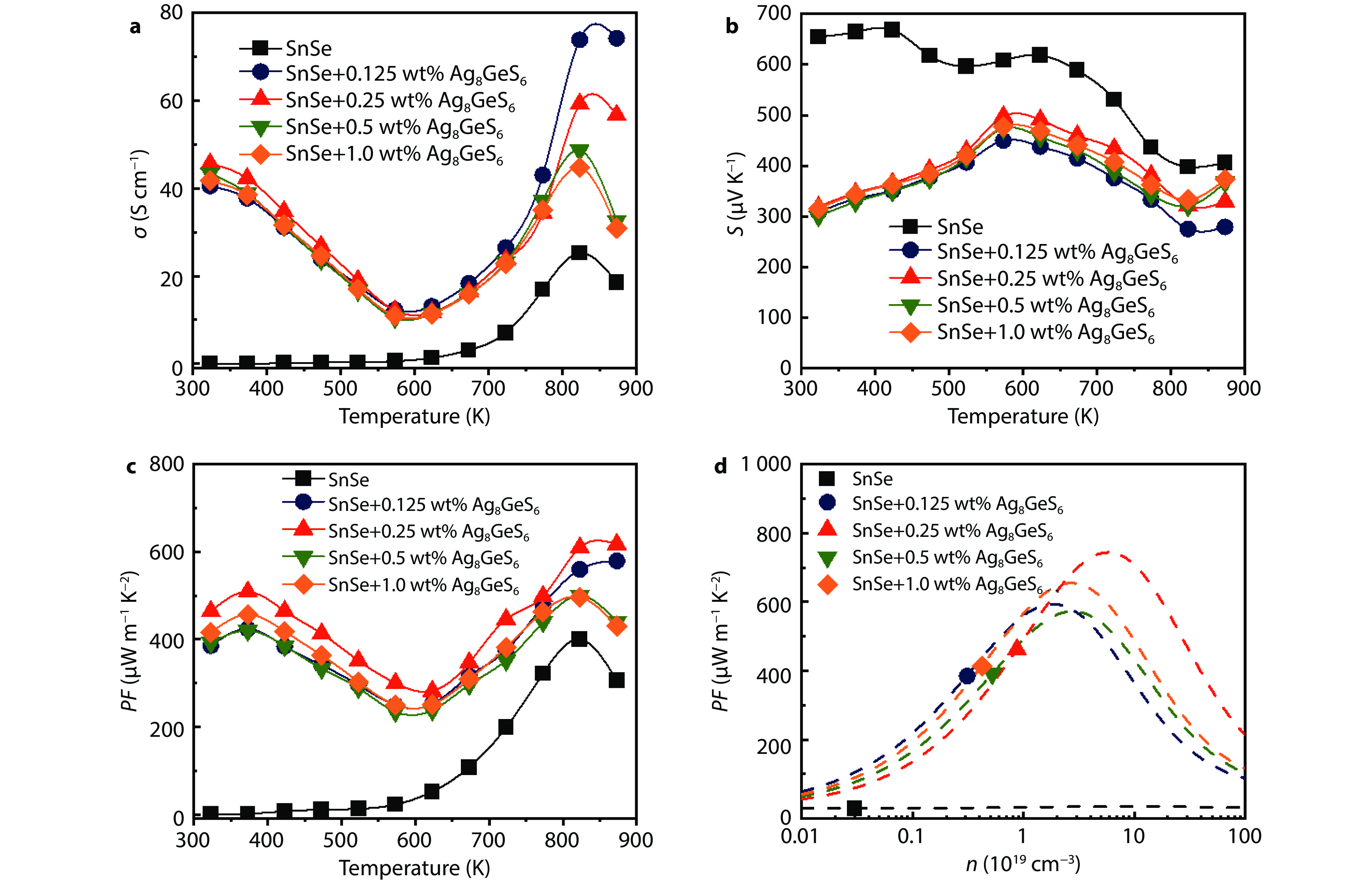
Figure 5.
Temperature dependence of electrical transport properties for the SnSe + x wt% Ag8GeS6 (x = 0, 0.125. 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0) samples in the parallel direction along the pressure direction: a Electrical conductivity, b Seebeck coefficient, c power factor, and d the relationship between carrier concentration (n) and power factor at room temperature based on SPB model
-
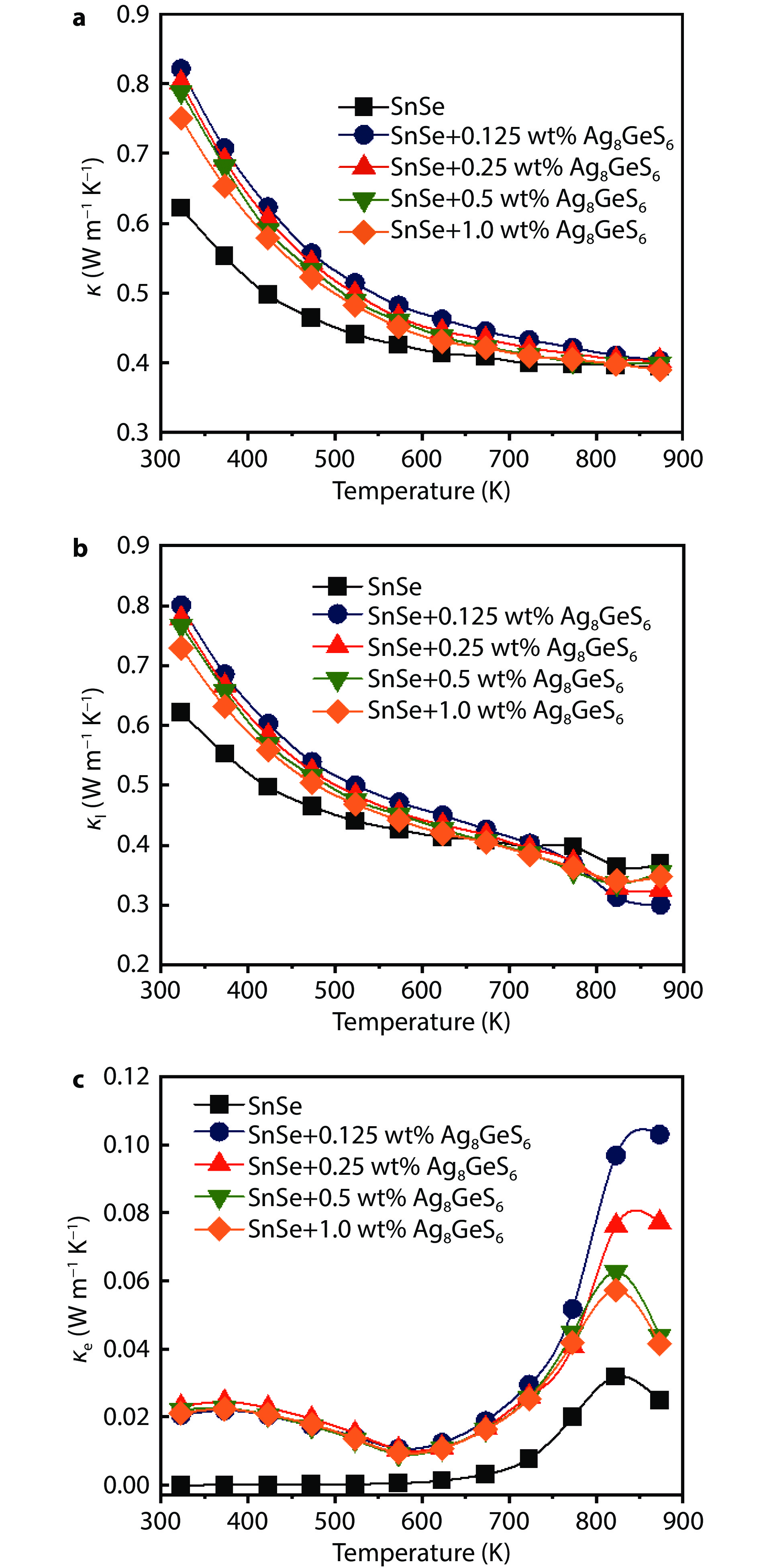
Figure 6.
Temperature dependence of thermal transport properties for the SnSe + x wt% Ag8GeS6 (x = 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 1.0) samples in the parallel direction along the pressure direction: a Total thermal conductivity (κ), b lattice thermal conductivity (κl), and c electron thermal conductivity (κe).
-
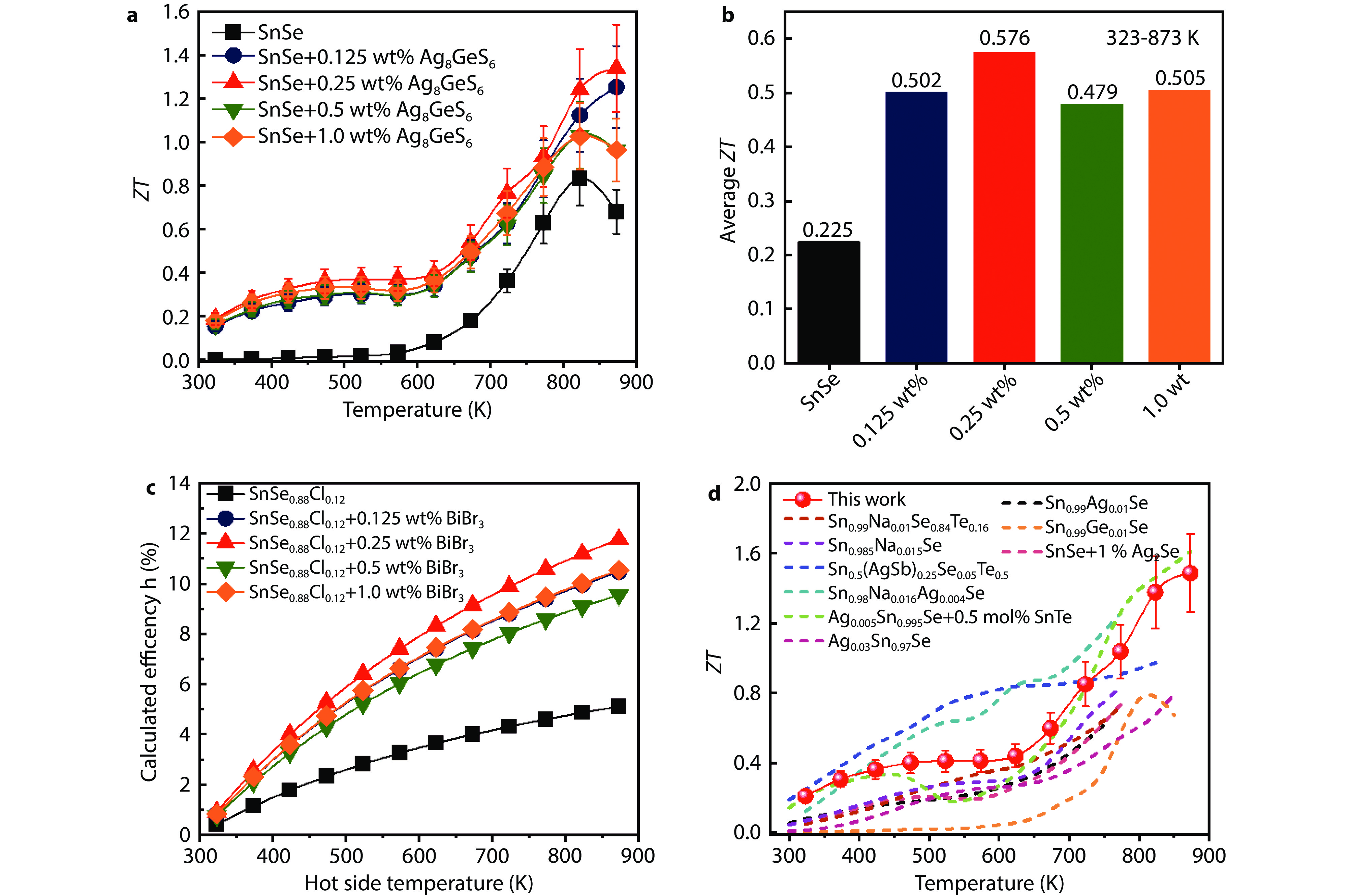
Figure 7.
a Temperature dependence of ZT values, b average ZT values, c theoretical calculation of conversion efficiency for the SnSe + x wt% Ag8GeS6 (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.5, and 1.0) samples, and d ZT values in comparison with other p-type polycrystalline SnSe materials.


 DownLoad:
DownLoad: